Gnss Gps - Initialization and Readings
This page provides a simple example of how to initialize and use the GNSS L86-M33 sensor with a Dasduino CONNECTPLUS.
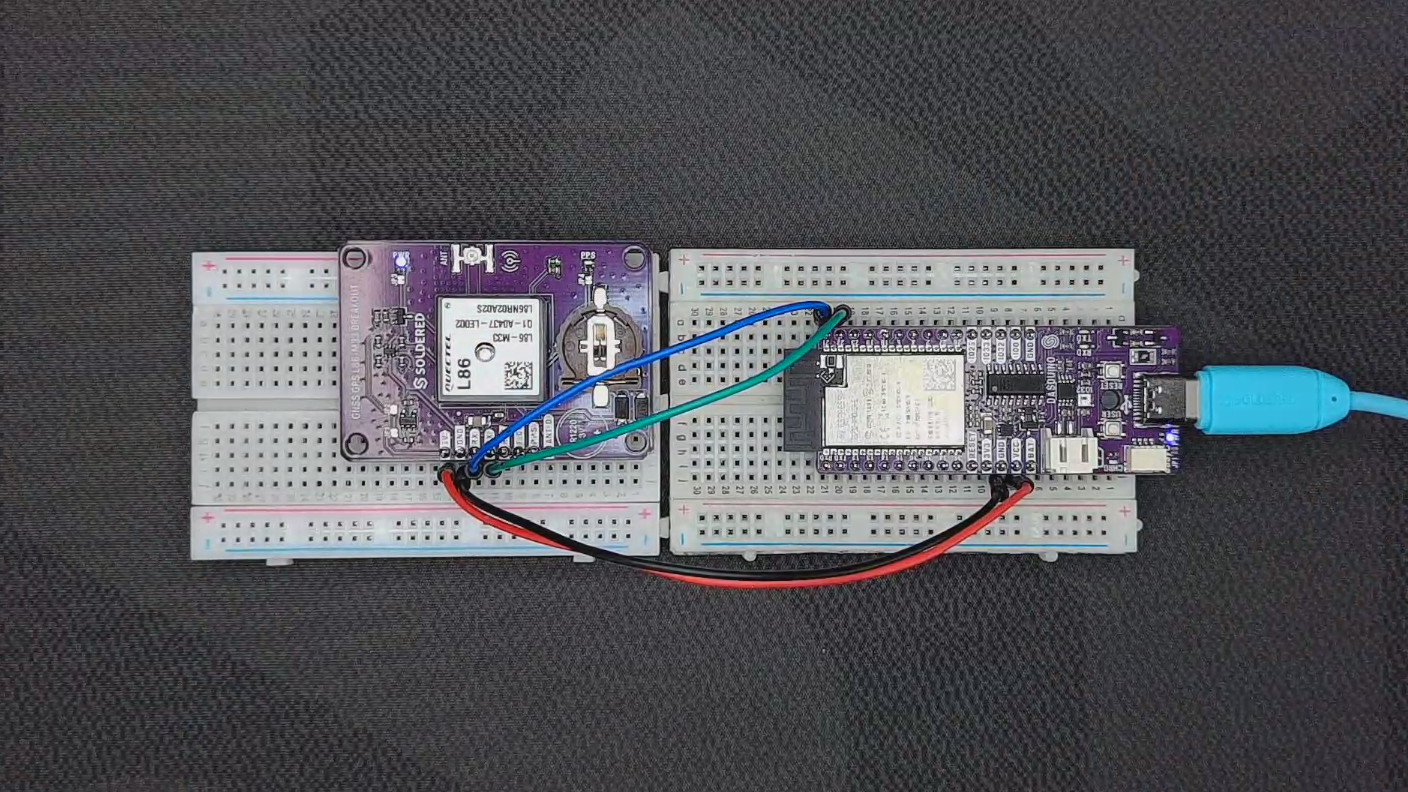
Initialization
To use the GNSS L86-M33 sensor with an Arduino, you need to include the appropriate library, define the communication pins, create an instance of the GNSS object, and initialize it within the setup() function. This ensures proper communication between the Arduino and the GNSS module. The begin() function is used to set up the sensor, allowing it to start receiving satellite data.
Here’s an example of how to initialize the GNSS L86-M33 sensor:
// Include the GNSS L86-M33 library
#include "GNSS-L86-M33-SOLDERED.h"
// Define pins for the GNSS module
#define GNSS_RX 3
#define GNSS_TX 4
// Create an object for the GNSS library
GNSS gps(GNSS_TX, GNSS_RX);
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication with the PC
gps.begin(); // Initialize the GNSS module
}
// ...
If you're using the Qwiic (easyC) version, you don't need to define RX and TX pins, so the initialization looks like this:
// Include the GNSS L86-M33 library
#include "GNSS-L86-M33-SOLDERED.h"
// Create the GNSS object
GNSS gnss;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication with the PC
gps.begin(); // Initialize the GNSS module
}
// ...
gps.begin()
Initializes the GNSS L86-M33 module, setting up communication over the defined serial pins and configuring the module for operation.
Returns value: Void
Basic Readings
This snippet provides an example of how to retrieve and display GNSS data using the L86-M33 module. The displayInfo() function reads latitude, longitude, date, and time from the GNSS module and prints them to the Serial Monitor. If the data is invalid, an error message is displayed. The table below summarizes the key functions used to extract GNSS information.
void displayInfo()
{
// Print out GPS latitude and longitude. If there is no valid data, show an error message.
Serial.print(F("Location: "));
if (gps.location.isValid())
{
Serial.print(gps.location.lat(), 6);
Serial.print(F(","));
Serial.print(gps.location.lng(), 6);
}
else
{
Serial.print(F("INVALID"));
}
// Print out time and date. If there is no valid data, show an error message.
Serial.print(F(" Date/Time: "));
if (gps.date.isValid())
{
Serial.print(gps.date.month());
Serial.print(F("/"));
Serial.print(gps.date.day());
Serial.print(F("/"));
Serial.print(gps.date.year());
}
else
{
Serial.print(F("INVALID"));
}
Serial.print(F(" "));
if (gps.time.isValid())
{
if (gps.time.hour() < 10)
Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.hour());
Serial.print(F(":"));
if (gps.time.minute() < 10)
Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.minute());
Serial.print(F(":"));
if (gps.time.second() < 10)
Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.second());
Serial.print(F("."));
if (gps.time.centisecond() < 10)
Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.centisecond());
}
else
{
Serial.print(F("INVALID"));
}
// Go to the new line, ready to print new data.
Serial.println();
}
isValid()
Checks if the GNSS location, date, or time data is valid.
Returns value: True if the respective data is valid, false otherwise.
| Function | Return Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
gps.location.lat() | double | Retrieves the latitude of the GNSS location. |
gps.location.lng() | double | Retrieves the longitude of the GNSS location. |
gps.date.month() | int | Retrieves the current month (1-12). |
gps.date.day() | int | Retrieves the current day (1-31). |
gps.date.year() | int | Retrieves the current year (e.g., 2025). |
gps.time.hour() | int | Retrieves the current hour (0-23). |
gps.time.minute() | int | Retrieves the current minute (0-59). |
gps.time.second() | int | Retrieves the current second (0-59). |
gps.time.centisecond() | int | Retrieves the current centisecond (0-99). |
Advanced Features
If you wish to activate AlwaysLocate™ Mode, Multi-tone AIC, and NMEA Message Filtering, you can send the appropriate commands after initializing the sensor. These features improve the accuracy and reliability of the GPS data, especially in challenging environments.
Here’s how to activate these advanced features:
// AlwaysLocate™ Mode Command
char alwaysLocateCmd[] = {"$PMTK225,8"};
// Multi-tone AIC Command
char multitoneAICCmd[] = {"$PMTK 286,1"};
// NMEA Message Filter Command
char nmeaMessageFilterCmd[] = {"$PMTK314,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0"};
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
gps.begin(); // Initialize the GNSS module
// Send commands to activate advanced features
gps.sendCommand(alwaysLocateCmd); // Activate AlwaysLocate™ Mode
gps.sendCommand(multitoneAICCmd); // Activate Multi-tone AIC
gps.sendCommand(nmeaMessageFilterCmd); // Filter NMEA messages
}
gps.sendCommand()
Sends a command to the GNSS module to configure advanced features like AlwaysLocate™ Mode, Multi-tone AIC, and NMEA message filtering.
Returns value: Void
Function parameters:
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | The command string to send to the GNSS module. |
Full Example
Open the Serial Monitor at 9600 baud to observe the detected data.
// Include L86-M33 GNSS Library
#include "GNSS-L86-M33-SOLDERED.h"
// Define pins for the GNSS module
#define GNSS_RX 3
#define GNSS_TX 4
// Create an object for the library called gps
GNSS gps(GNSS_TX, GNSS_RX);
// Variable that keeps track of the last time GNSS data was displayed on serial.
unsigned long lastGnssDisplay = 0;
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial communication for the Serial Monitor at 9600 baud. A higher baud rate can cause problems while sending a command.
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize the L86-M33 library.
gps.begin();
}
void loop()
{
// If there is any data on the UART of the GNSS, read it and send every character to the library
while (gps.gnssSerial->available() > 0)
{
// If something is successfully decoded, display new data.
if (gps.encode(gps.gnssSerial->read()))
{
// Check if 500 milliseconds have passed since the last data display.
if ((unsigned long)(millis() - lastGnssDisplay) > 500UL)
{
// Capture new timestamp.
lastGnssDisplay = millis();
// Display new data.
displayInfo();
}
}
}
// No data within the first 5 seconds after startup? Something might be wrong—please check the wiring!
if (millis() > 5000 && gps.charsProcessed() < 10)
{
Serial.println(F("No GPS detected: check wiring."));
while (true)
{
// Delay is needed for the ESP8266.
delay(10);
}
}
}
// Function that displays decoded data from the GNSS library.
void displayInfo()
{
// Print out GPS latitude and longitude. If there is no valid data, show an error message.
Serial.print(F("Location: "));
if (gps.location.isValid())
{
Serial.print(gps.location.lat(), 6);
Serial.print(F(","));
Serial.print(gps.location.lng(), 6);
}
else
{
Serial.print(F("INVALID"));
}
// Print out time and date. If there is no valid data, show an error message.
Serial.print(F(" Date/Time: "));
if (gps.date.isValid())
{
Serial.print(gps.date.month());
Serial.print(F("/"));
Serial.print(gps.date.day());
Serial.print(F("/"));
Serial.print(gps.date.year());
}
else
{
Serial.print(F("INVALID"));
}
Serial.print(F(" "));
if (gps.time.isValid())
{
if (gps.time.hour() < 10)
Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.hour());
Serial.print(F(":"));
if (gps.time.minute() < 10)
Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.minute());
Serial.print(F(":"));
if (gps.time.second() < 10)
Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.second());
Serial.print(F("."));
if (gps.time.centisecond() < 10)
Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.centisecond());
}
else
{
Serial.print(F("INVALID"));
}
// Move to a new line, ready to print new data.
Serial.println();
}
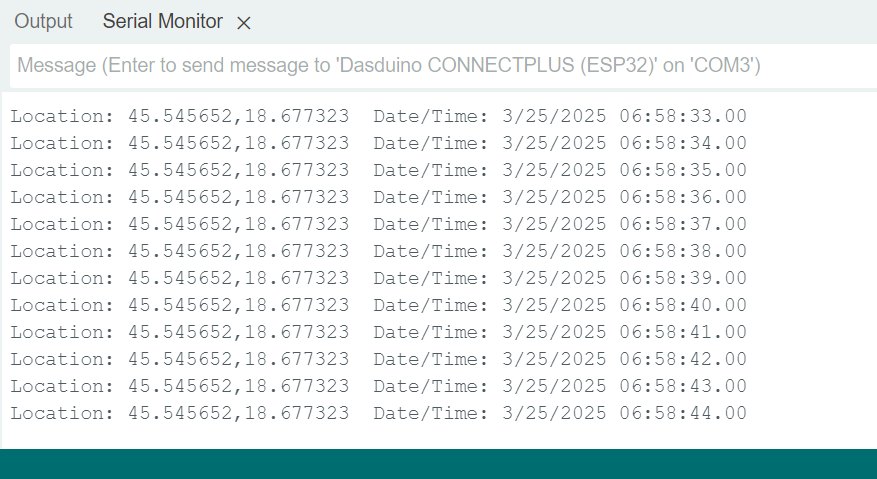
L86_M33_Basic_Readings.ino
Example file for using the GNSS-GPS L86-M33
L86_M33_easyC_Basic_Readings.ino
Example file for using the GNSS-GPS L86-M33 with easyC
L86_M33_Advanced_Example.ino
Example file for using the GNSS-GPS L86-M33 with advanced features
L86_M33_easyC_Advanced_Example.ino
Example file for using the GNSS-GPS L86-M33 easyC with advanced features