LSM6DS – Measuring linear acceleration with LSM6DS3 Accelerometer (example)
This page contains some simple examples with function documentation on how to take accelerometer measurements using the LSM6DS3 Accelerometer & Gyroscope.
Initialization
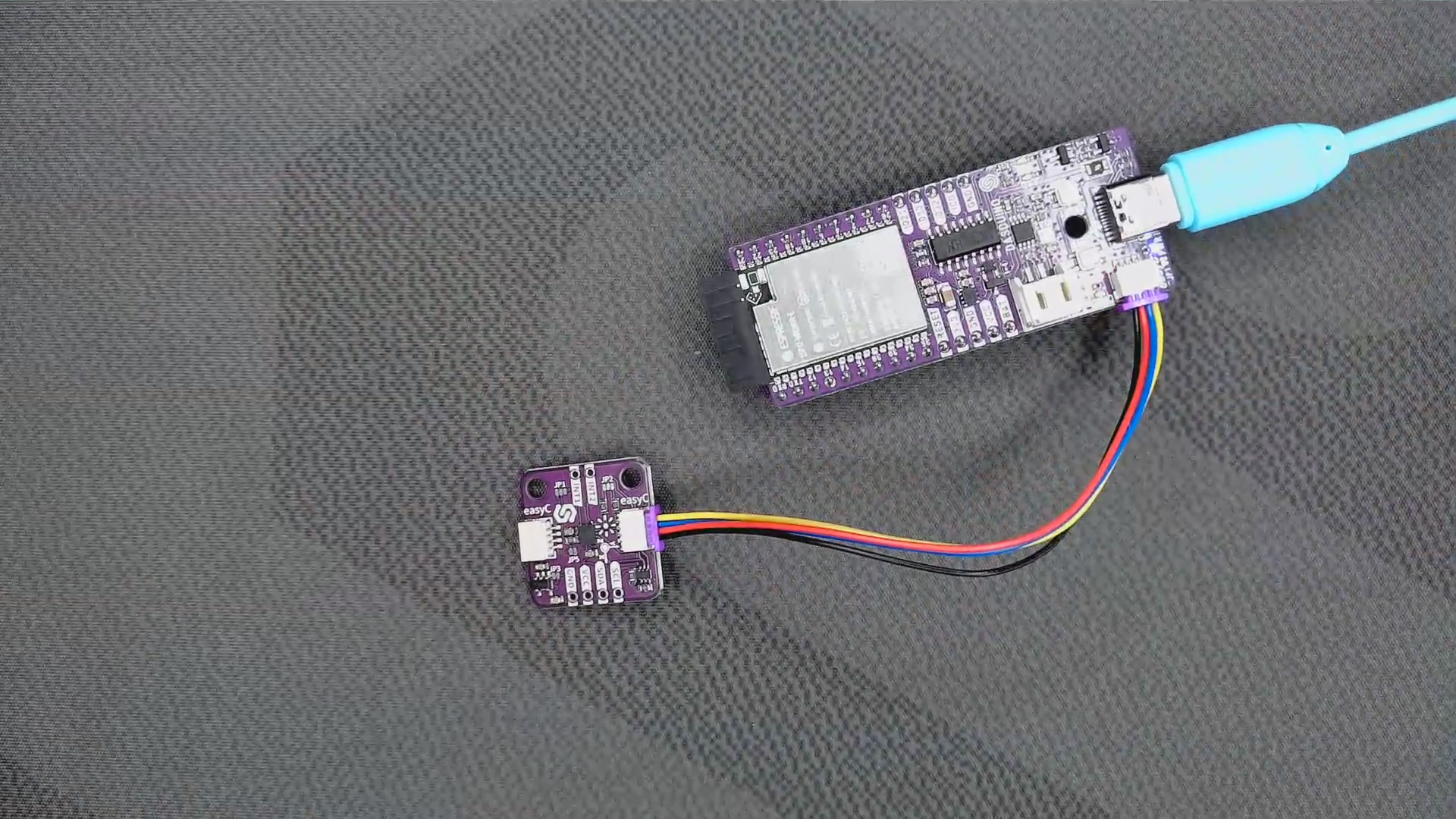
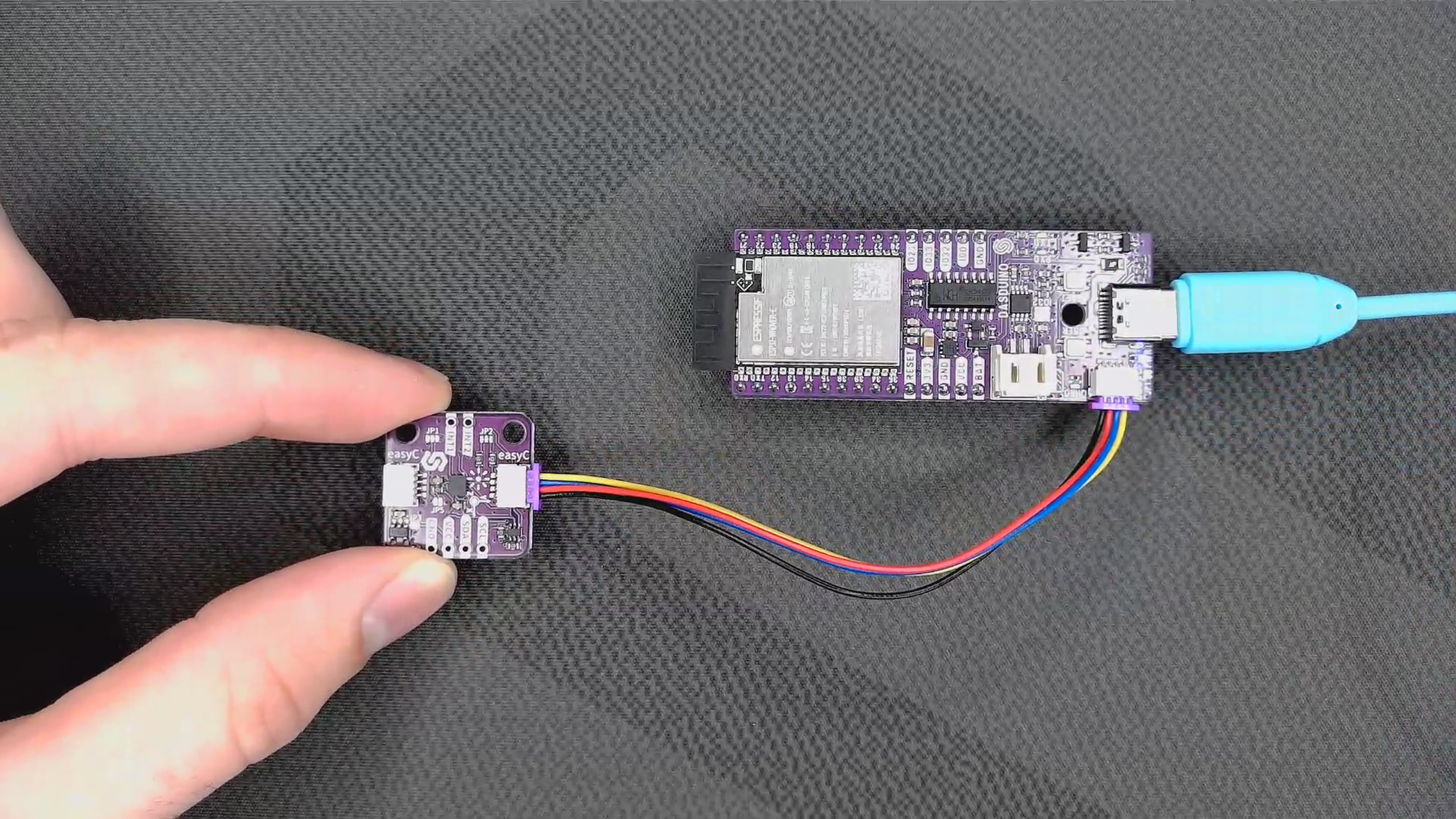
To start working with the Accelerometer & Gyroscope LSM6DS 6-DOF Breakout, you need to set up your Arduino environment. First, include the required library, create the sensor object, and initialize the sensor in the setup() function. You can use the return value of begin() to check if everything is connected correctly:
// Include libraries
#include "LSM6DS3-SOLDERED.h"
#include "Wire.h"
// Create an LSM6DS3 object
Soldered_LSM6DS3 myIMU; // Default address is 0x6B
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(1000); // Relax...
// Initialize sensor
if (!myIMU.begin())
{
// 'begin' returned false, there is an error
Serial.println("Can't initialize LSM6DS!");
Serial.println("Check connection!");
while (true)
;
}
Serial.println("LSM6DS initialized successfully.");
}
//...
myIMU.begin()
Initializes the **LSM6DS Accelerometer & Gyroscope sensor**, setting up communication over I2C or SPI and configuring the sensor for operation. This function also verifies the presence of the sensor on the specified I2C address or SPI bus.
Returns value: **Returns `true`**: If initialization is successful, indicating that the sensor is properly connected and configured. - **Returns `false`**: If initialization fails, indicating a connection issue or incorrect configuration.
Measuring acceleration
To start measuring velocity information, we first need to read all 3 (x, y, z) directional vectors and display them as shown below.
// Read acceleration and print it on serial
Serial.print("ACCX:");
Serial.print(myIMU.readFloatAccelX(), 4);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print("ACCY:");
Serial.print(myIMU.readFloatAccelY(), 4);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print("ACCZ:");
Serial.print(myIMU.readFloatAccelZ(), 4);
Serial.print(",");
myIMU.readFloatAccel*(),4;
Reads the acceleration value along the given axis from the LSM6DS3 sensor.
Returns value: Returns a floating-point number in units of g (gravitational force).
Full example
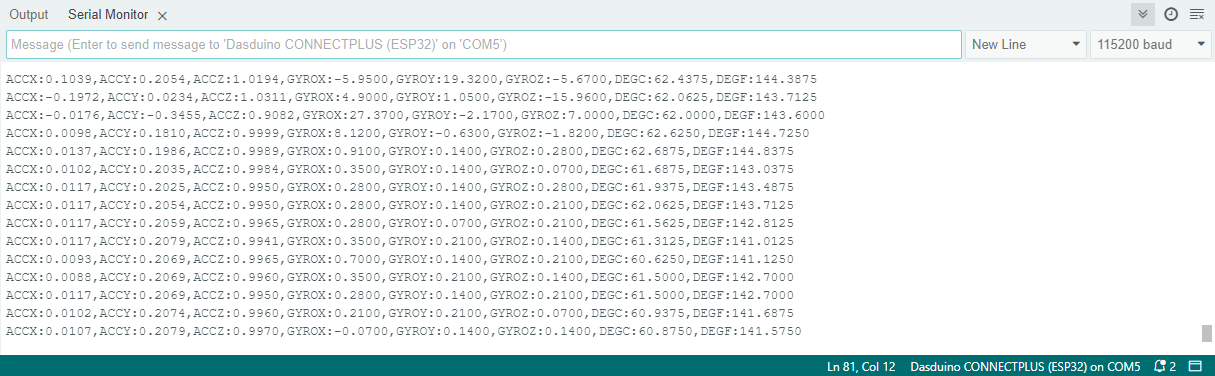
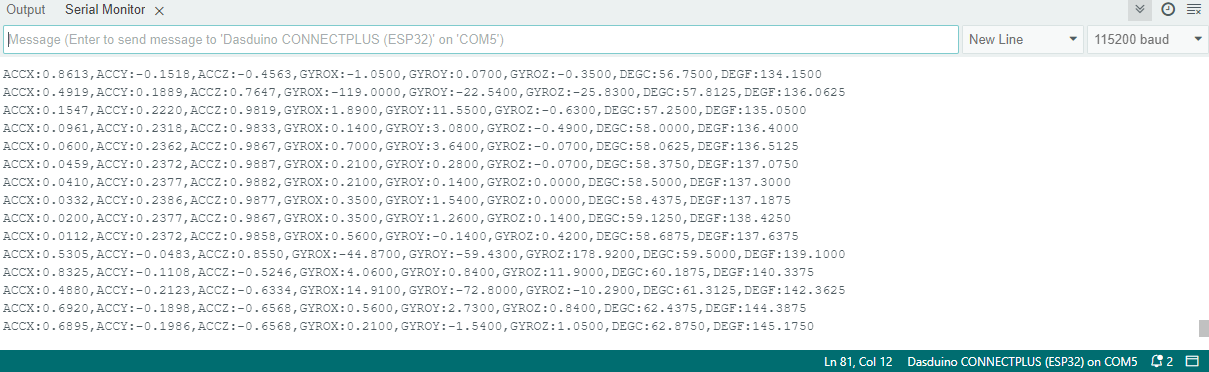
Try all of the aforementioned functions in this full example, which prints out the measured acceleration over Serial at 115200 baud:
// Include libraries
#include "LSM6DS3-SOLDERED.h"
#include "Wire.h"
// Create object from LSM library
Soldered_LSM6DS3 myIMU; // Default address is 0x6B
void setup()
{
// Init serial communication
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(1000); // Relax...
// Call .begin() to configure the IMU
myIMU.begin();
}
void loop()
{
// Get all parameters and print them on the Serial Monitor
// Read acceleration and print it on serial
Serial.print("ACCX:");
Serial.print(myIMU.readFloatAccelX(), 4);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print("ACCY:");
Serial.print(myIMU.readFloatAccelY(), 4);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print("ACCZ:");
Serial.print(myIMU.readFloatAccelZ(), 4);
Serial.print(",");
delay(150);
}
minimalistExample.ino
Most basic example of use. Example using the LSM6DS3 with basic settings