Adc - Initialization and Simple ADC Read
This page provides various examples on using the ADS1015/ADS1115 analog-to-digital converters (ADC) with Arduino, covering initialization and reading analog inputs.
Initialization and Gain
This section initializes the ADS1015/ADS1115 sensor, setting up communication and preparing the ADC for use. It also configures the gain, which adjusts the input voltage range, ensuring optimal resolution and accuracy for the ADC readings based on the expected signal levels.
Since the Arduino libraries work generally the same, let's overview examples for ADS1115 here. Make sure to include the correct library for your sensor!
#include "ADS1115-SOLDERED.h"
ADS1115 ADS;
or
#include "ADS1015-SOLDERED.h"
ADS1015 ADS;
#include "ADS1115-SOLDERED.h"
// Declare your ADC object
ADS1115 ADS;
void setup()
{
// Initialize the Serial communication
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(__FILE__);
Serial.print("ADS1X15_LIB_VERSION: ");
Serial.println(ADS1X15_LIB_VERSION);
// Initialize the ADC
ADS.begin();
}
void loop()
{
// Set the gain
ADS.setGain(0);
}
// ...
ADS.begin()
Initializes the ADS1115 sensor, setting up I2C communication and configuring the sensor for data acquisition.
Returns value: True if initialization is successful, false otherwise.
ADS.setGain()
Sets the gain for the ADS1115 to adjust the input voltage range.
Returns value: True if the gain is successfully set, false otherwise.
Function parameters:
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
ADSGain | gain | The gain value to be set for the sensor. |
Simple ADC Read
This example demonstrates how to read the values from all four analog input channels (AIN0 to AIN3) using the ADS1115.
#include "ADS1115-SOLDERED.h"
// Declare your ADC object
ADS1115 ADS;
void setup()
{
// Initialize the Serial communication
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(__FILE__);
Serial.print("ADS1X15_LIB_VERSION: ");
Serial.println(ADS1X15_LIB_VERSION);
// Initialize the ADC
ADS.begin();
}
void loop()
{
// Set the gain
ADS.setGain(0);
// Read the values from each analog input channel
int16_t val_0 = ADS.readADC(0);
int16_t val_1 = ADS.readADC(1);
int16_t val_2 = ADS.readADC(2);
int16_t val_3 = ADS.readADC(3);
// Calculate voltage from raw ADC values
float f = ADS.toVoltage(1); // Voltage factor
Serial.print("\tAnalog0: ");
Serial.print(val_0);
Serial.print('\t');
Serial.println(val_0 * f, 3);
Serial.print("\tAnalog1: ");
Serial.print(val_1);
Serial.print('\t');
Serial.println(val_1 * f, 3);
Serial.print("\tAnalog2: ");
Serial.print(val_2);
Serial.print('\t');
Serial.println(val_2 * f, 3);
Serial.print("\tAnalog3: ");
Serial.print(val_3);
Serial.print('\t');
Serial.println(val_3 * f, 3);
Serial.println();
delay(1000);
}
ADS.readADC()
Reads an ADC value from the ADS1115 sensor. It can read either single-ended or differential values, depending on the provided input.
Returns value: The raw ADC value read from the sensor. The value represents the measured voltage or differential voltage, depending on the mode.
Function parameters:
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
uint8_t | channel1 | The first input channel to read from (0 to 3 for single-ended mode or channel pair for differential mode). |
uint8_t | channel2 | The second input channel to read from, used only in differential mode (optional). |
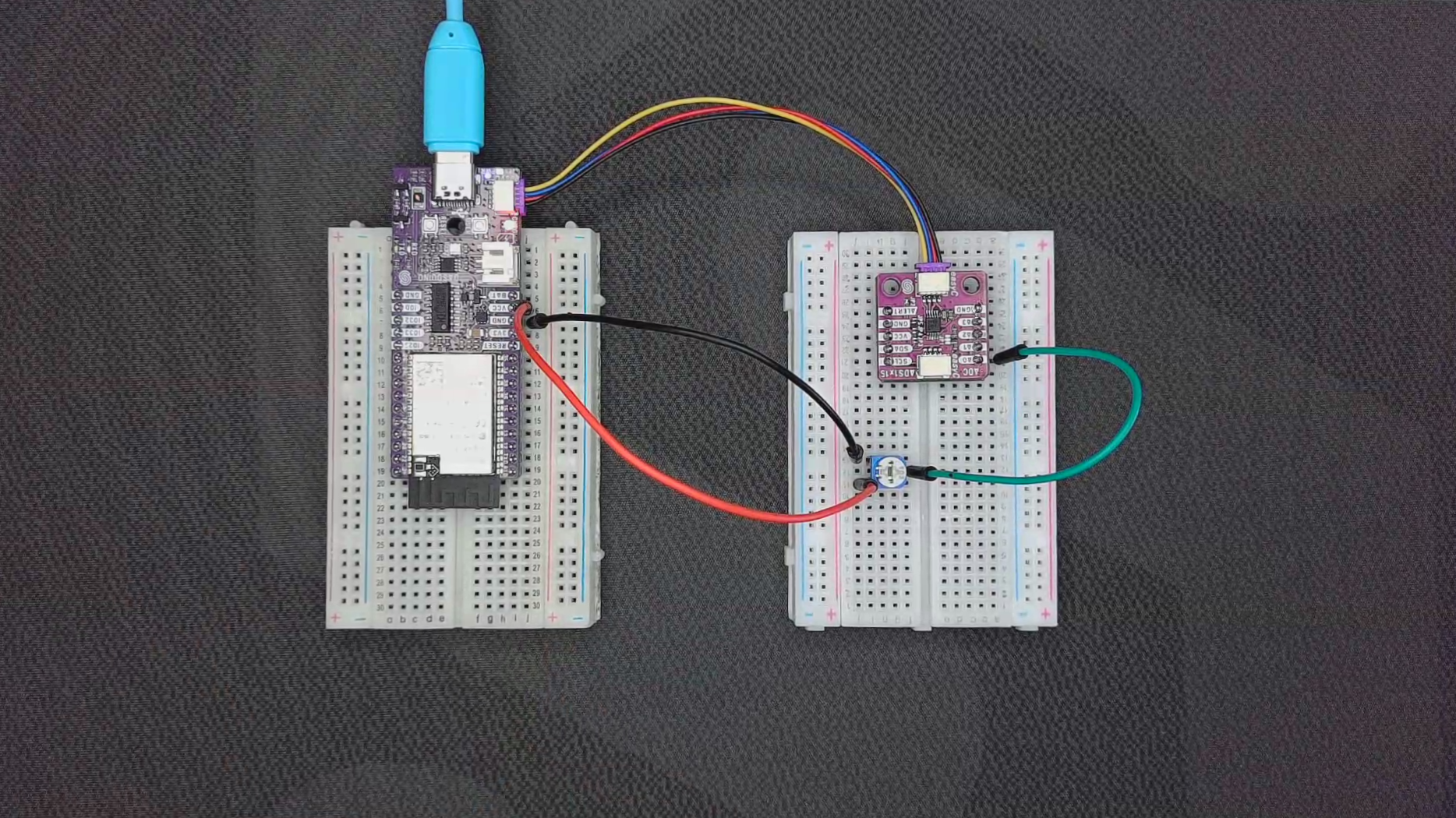

ADC_read.ino
Example files for using the ADC ADS1x15 sensors.