Bme680 – How it works
BME680 is an integrated circuit by Bosch. When using our board, you are essentially communicating with the onboard BME680 directly via I2C communication.
Datasheet
For an in-depth look at technical specifications, refer to the official BME680 Datasheet:
BME680 Datasheet
Detailed technical documentation for the BME680 sensor
How the sensor works
The BME680 is an environmental & air quality sensor with temperature, barometric pressure, humidity, and gas resistance.
Temperature and humidity sensors work by measuring the capacitance or resistance of air samples. Most of these sensors utilize capacitive measurement to determine the amount of dampness in the air. This sort of measurement relies on two electrical conductors with a non-conductive polymer film laid between them to form an electrical field.
Moisture from the air collects on the film and causes changes in the voltage levels between the two plates. This change is then converted into a computerized measurement of the air’s relative humidity after taking the air temperature into account.
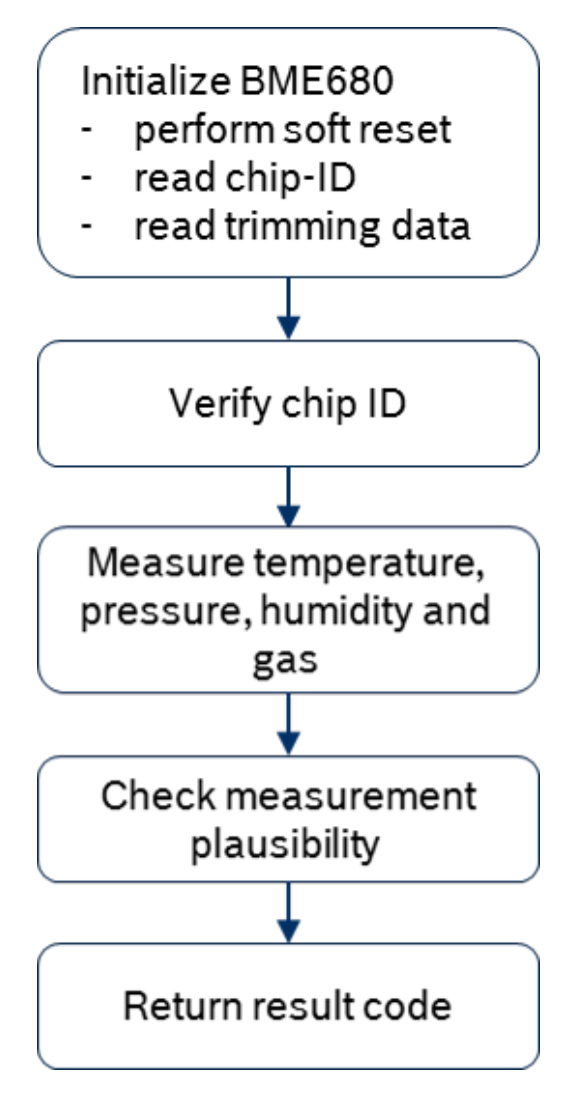
The BME680 also supports a self test on soft reset, as pictured below:
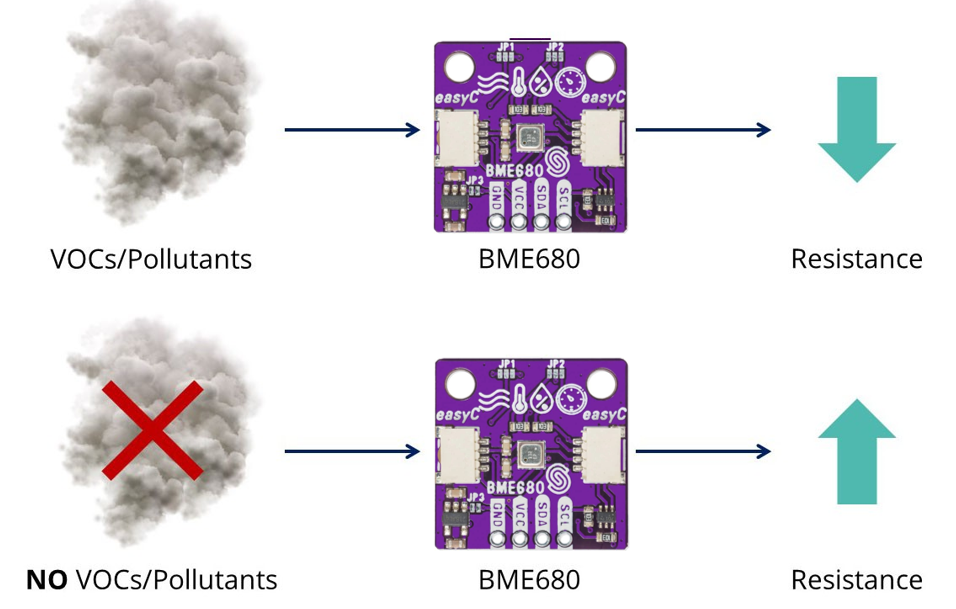
The Gas resistance sensor works as follows: Based on the volume and concentration of a gas in an area, the sensor will produce what is called a “corresponding potential difference,” which changes the level of resistance of the material inside the sensor. From this change in the level of resistance comes an electrical signal that is measured as output voltage.
I2C communication
The BME680 uses the I2C protocol to communicate with a microcontroller. It operates with a fixed I2C address of 0x76.
Upon request, the sensor responds with pressure and temperature values in a 20-bit format and the humidity value as a 16-bit ADC value.