Logic Level Converter - How it works
The Logic Level Converter Board by Soldered enables safe voltage level shifting between 3.3V and 5V logic systems, facilitating communication between devices with differing voltage requirements. Using MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) for bidirectional signal conversion, the board supports multiple communication protocols, including I2C, SPI, and UART.
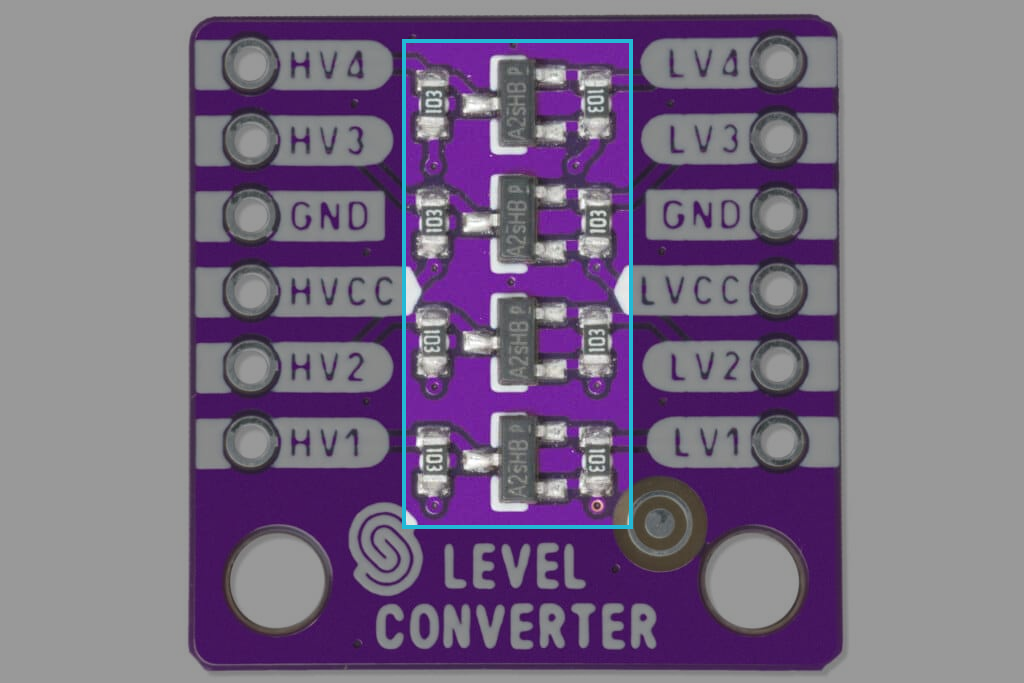
MOSFET logic level shift
MOSFET logic level shifting is an efficient method to safely translate signals between devices with different voltage levels. It uses MOSFETs to allow signals to pass from high-voltage systems (e.g., 5V) to low-voltage systems (e.g., 3.3V) while ensuring the safety of the low-voltage components.
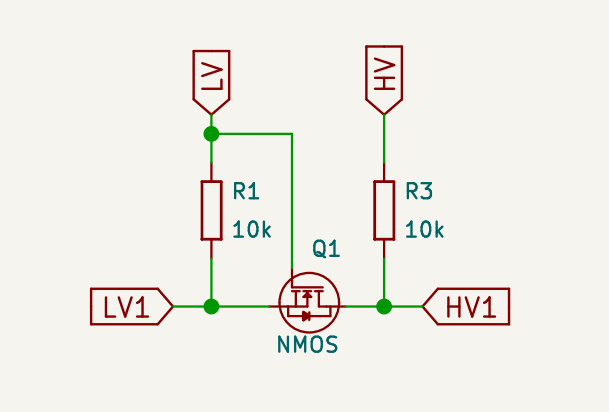
The key to bidirectional MOSFET logic level shifting lies in the use of pull-up resistors and the MOSFET’s switching capabilities. Here’s how it works:
- Pull-up Resistors: When the MOSFET is off (no voltage applied to the gate), the pull-up resistors pull the signal to the high voltage level (e.g., 5V). This ensures that the signal remains at the correct logic level for the high-voltage side when it's not actively being driven by the low-voltage device.
- MOSFET Switching: When the low-voltage device (e.g., 3.3V microcontroller) needs to send a low signal, it pulls the gate of the MOSFET low, turning it on. This allows current to flow from the high-voltage side to the low-voltage side. In this state, the MOSFET switches the signal from high to low, enabling the low-voltage device to send a low signal.
- Bidirectional Functionality: For bidirectional communication (such as in I2C), when the high-voltage side wants to send a low signal, the MOSFET allows the current to flow in the opposite direction. The pull-up resistor on the low-voltage side ensures the signal returns to the high state once the MOSFET is turned off.
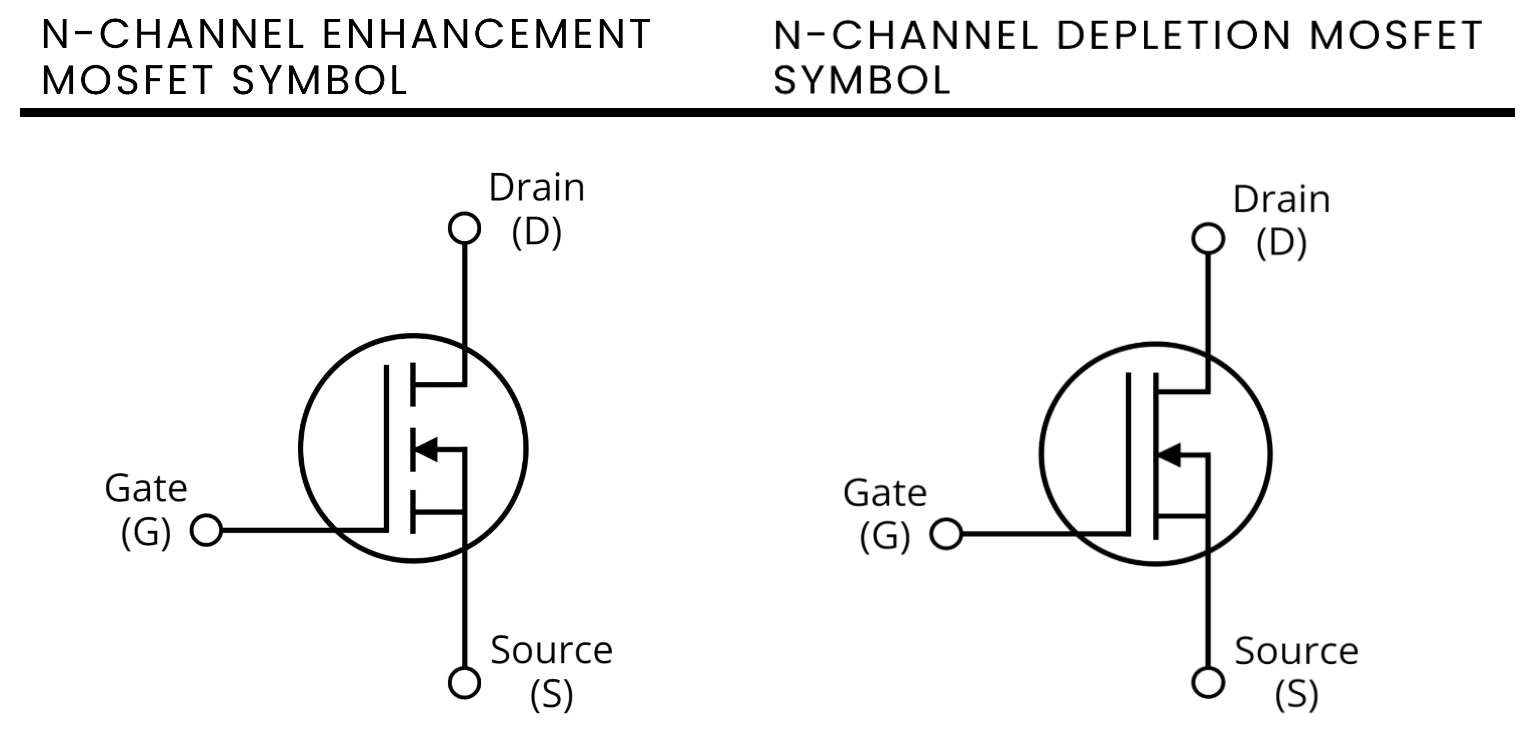
Enhancing and depleting modes refer to how MOSFETs operate based on the voltage applied to the gate. In enhancement mode, a positive voltage at the gate creates a conductive channel between the source and drain, allowing current to flow. In depletion mode, the gate voltage depletes the channel, reducing or stopping current flow.
MOSFET logic level shifting is commonly used for protocols like I2C, SPI, and UART, where bidirectional communication is needed. The I2C bus, for example, requires safe voltage translation in both directions to prevent damage to low-voltage devices.