MCP47A1 - Setting specific voltages
We can set the DAC to output a specific voltage at any time.
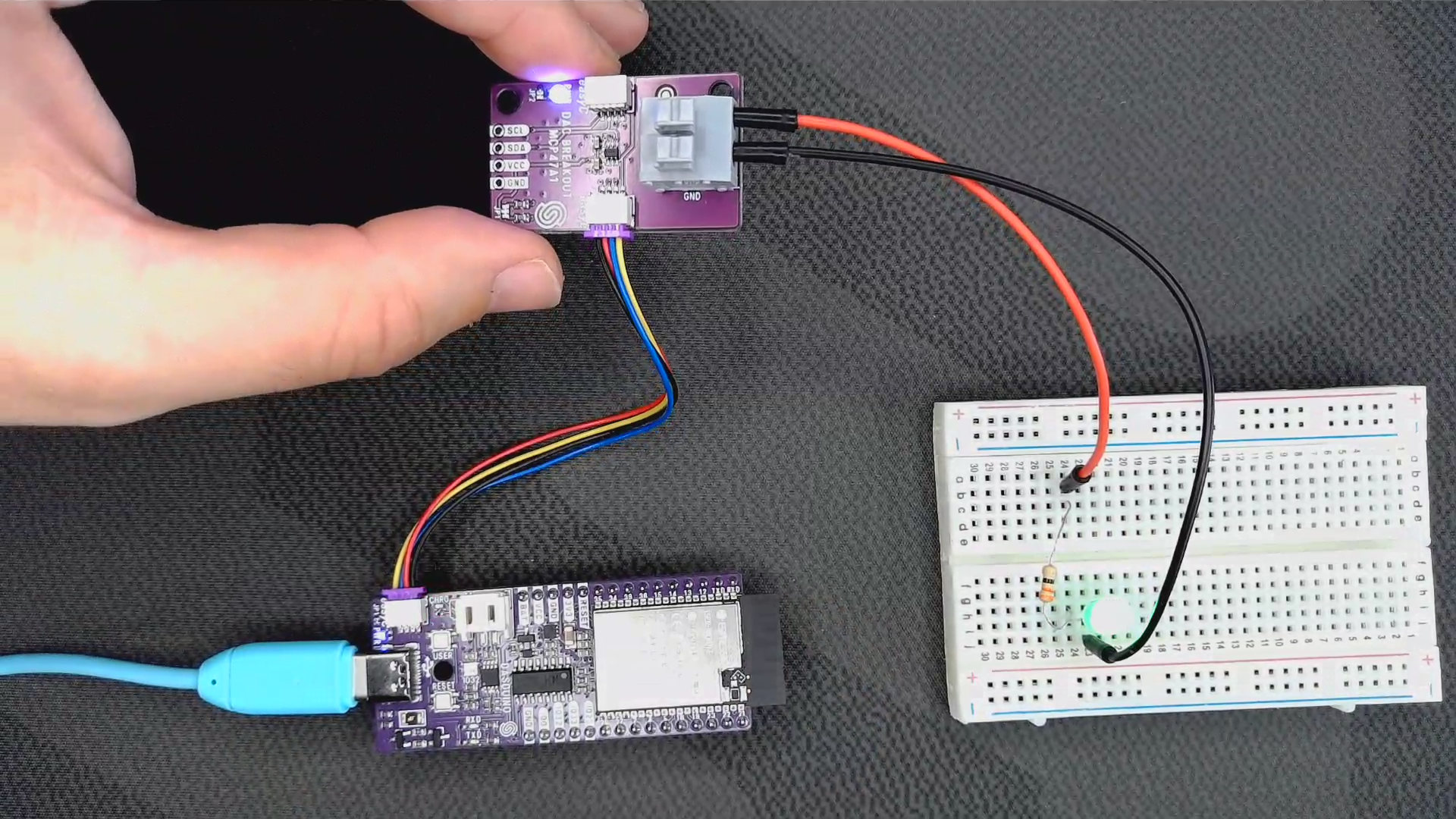
Connections for each example
First, we have to include the library and create an instance of the DAC object:
#include "MCP47A1-SOLDERED.h" // Include Soldered library for MCP47A1 DAC.
MCP47A1_SOLDERED dac; // Create an instance of the object
Next, in the setup() function, we initialize the I2C communication with the DAC:
void setup()
{
dac.begin(); // Initialize the DAC library.
}
dac.begin()
Initializes the I/O DAC via I2C
Returns value: None
Finally, in the loop() function, we can hook up an LED to the VOUT and GND connectors and change the voltage every 2 seconds:
void loop()
{
float volts;
// Set DAC output voltage to 0 V
volts = 0;
dac.setVoltage(volts);
delay(2000);
// Set DAC output voltage to 1 V
volts = 1;
dac.setVoltage(volts);
delay(2000);
// Set DAC output voltage to 2.5 V
volts = 2.5;
dac.setVoltage(volts);
delay(2000);
// Set DAC output voltage to 3.3 V
volts = 3.3;
dac.setVoltage(volts);
delay(2000);
}
dac.setVoltage(float _volts)
Sets the voltage at the DAC's output.
Returns value: None
Function parameters:
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
float | _volts | Voltage at the DAC's output in the range from 0V to VCC. |
Full example
See the full example below:
#include "MCP47A1-SOLDERED.h" // Include Soldered library for MCP47A1 DAC.
MCP47A1_SOLDERED dac; // Create an instance of the object
void setup()
{
dac.begin(); // Initialize the DAC library.
}
void loop()
{
float volts;
// Set DAC output voltage to 0 V
volts = 0;
dac.setVoltage(volts);
delay(2000);
// Set DAC output voltage to 1 V
volts = 1;
dac.setVoltage(volts);
delay(2000);
// Set DAC output voltage to 2.5 V
volts = 2.5;
dac.setVoltage(volts);
delay(2000);
// Set DAC output voltage to 3.3 V
volts = 3.3;
dac.setVoltage(volts);
delay(2000);
}