Simple Soil Sensor - How it works
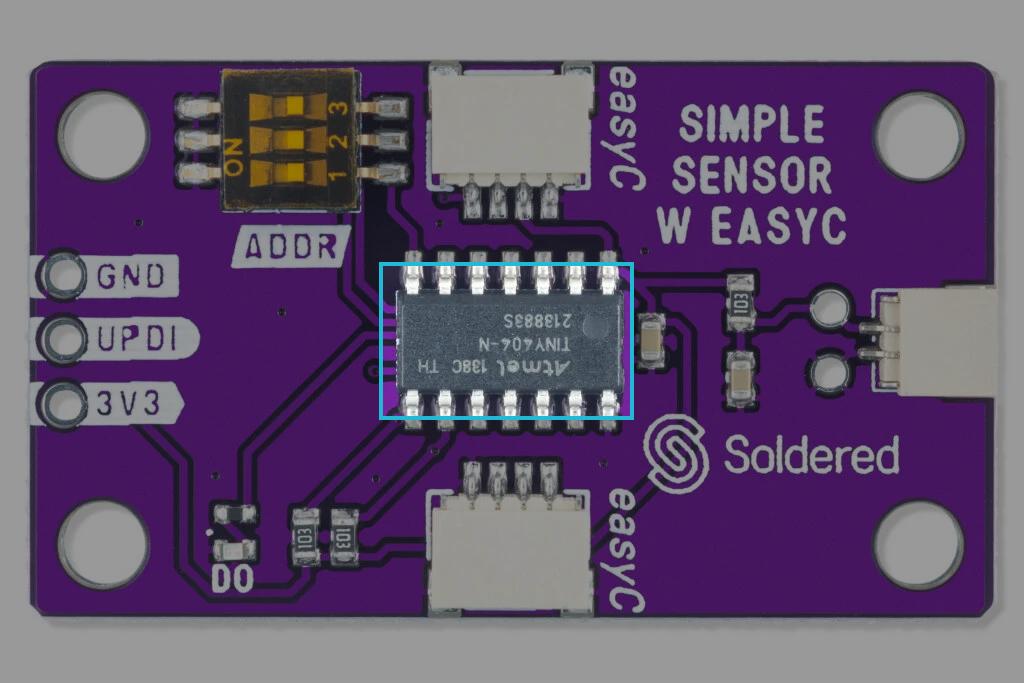
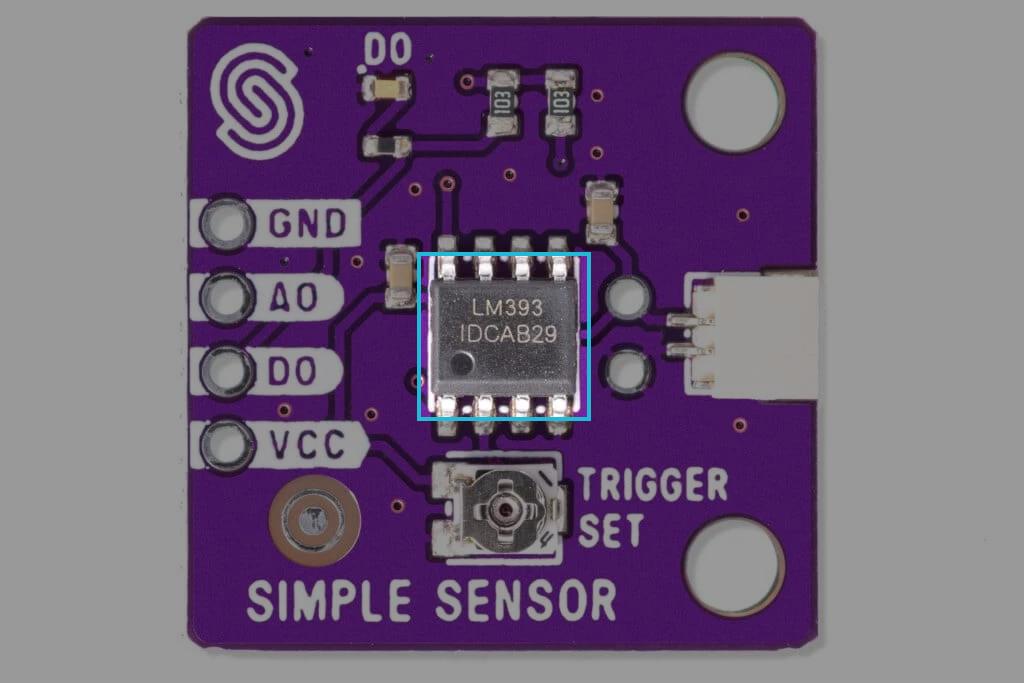
Both the regular and Qwiic versions of the sensor use an external breakout board with 2 exposed nickle-plated prongs. The difference between them is the onboard IC, which processes the provided data. The regular version uses a simple LM393 voltage comparator by Texas Instruments, while the Qwiic version uses an ATTiny404 MCU to process the data and implement I2C communication.
DataSheet
For an in-depth look at technical specifications, refer to the official ATTiny404 / LM393 Datasheet:
ATTiny404 Datasheet
Detailed technical documentation for the LM393 Voltage Comparator.
LM393 Datasheet
Detailed technical documentation for the ATTiny404 microcontroller.
How the sensor works
The soil humidity sensor uses an extarnal breakout board that contains two exposed nickle-plated prongs. As soil gets more humid, the resistance becomes smaller and the internal voltage between the prongs gets bigger. The sensor includes an IC to provide additional functionality and simplify its operation.
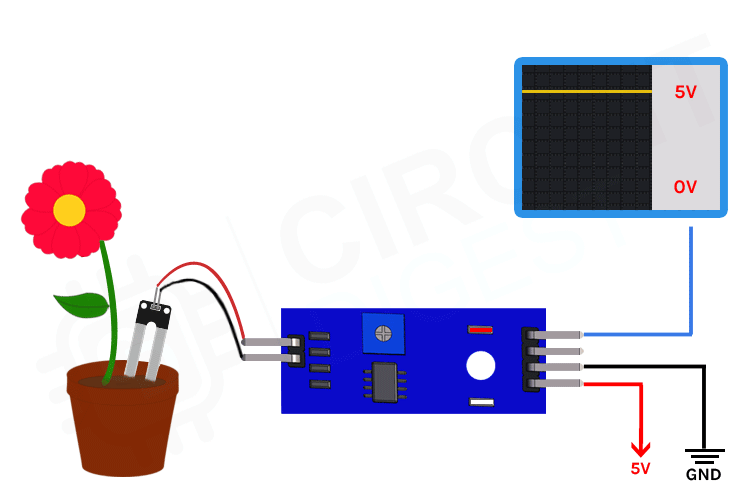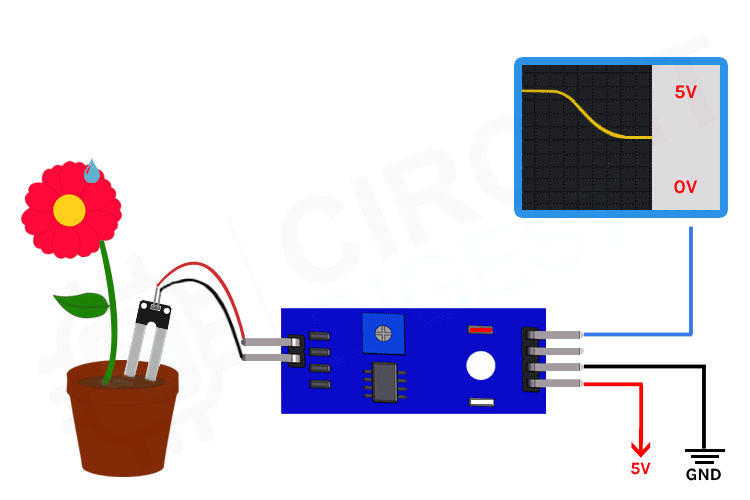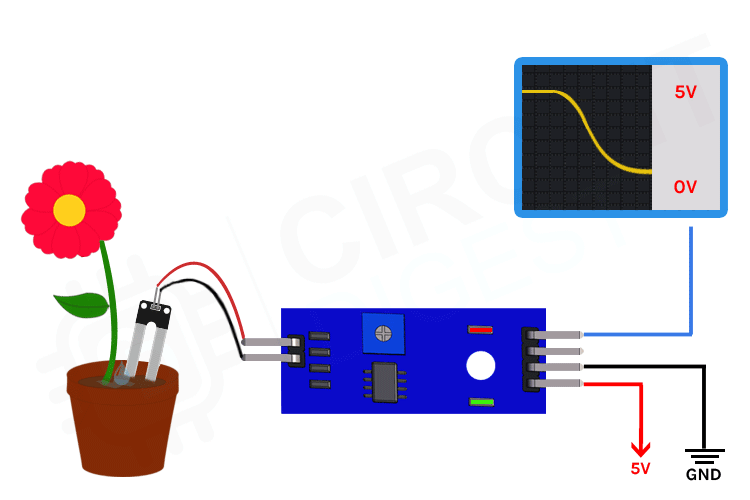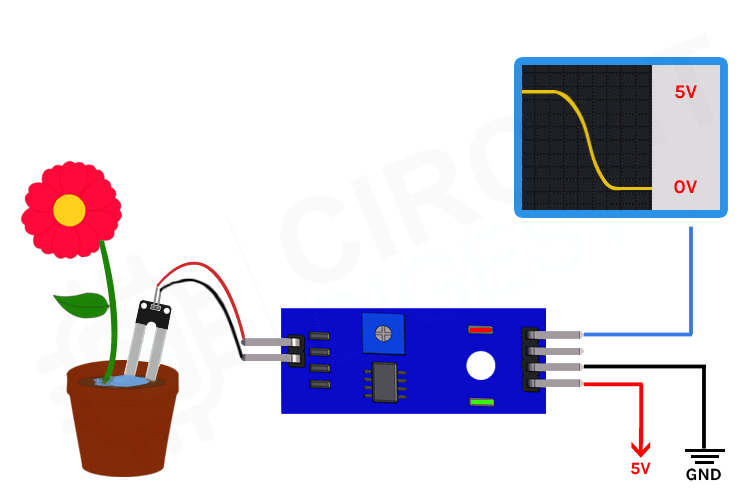
I2C communication - Qwiic
Qwiic versions of the product use onboard ATTINY404 MCU to implement I2C communication. Breakout board operates with a default I2C address of 0x30 but can be changed with onboard switches,to change breakout board's address, check the Address selection. When detected, ATTINY404 recives data from sensor and passes it to the main MCU using I2C data line. To check in detail how to ATTINY404 is preprogrammed, check firmware github page.