How it works
The SPK0641HT4H-1 is a compact digital MEMS microphone manufactured by Syntiant, designed to deliver high performance and low power consumption in a tiny top-port package. On this breakout board, the system communicates directly with the onboard SPK0641HT4H-1 through a PDM (Pulse Density Modulation) digital audio interface, eliminating the need for analog signal paths and external ADCs.
Inside the device, a MEMS acoustic transducer, low-noise input buffer, and sigma-delta modulator work together to convert incoming sound pressure into a 1-bit digital signal. The digital nature of this output minimizes interference and allows the microphone to connect directly to microcontrollers or audio processors that support PDM input. The result is a high-fidelity, low-noise capture of sound across a wide frequency range, ideal for applications like voice recognition, smart speakers, and portable audio devices.
Datasheet
For detailed technical specifications, refer to the official SPK0641HT4H-1 Datasheet:
SPK0641HT4H-1 Datasheet
Detailed technical documentation for the SPK0641HT4H-1 Digital MEMS Microphone
PDM Communication
Unlike analog microphones that produce a continuously varying voltage, the SPK0641HT4H-1 outputs sound as a digital PDM stream — a high-frequency sequence of ones and zeros whose density represents the instantaneous amplitude of the sound wave. This digital encoding provides excellent noise immunity and simplifies system design, as the signal can be processed directly by a codec or microcontroller with a PDM interface.
During operation, the CLK pin receives the clock signal from the host device (typically between 1 MHz and 4.8 MHz), which synchronizes data sampling and transmission. The DATA pin outputs the PDM bitstream in step with this clock. The SEL pin determines which channel the microphone outputs to when multiple units share the same data line — a logic high selects the left channel, and a low selects the right channel. This simple arrangement enables the creation of stereo systems with minimal wiring.
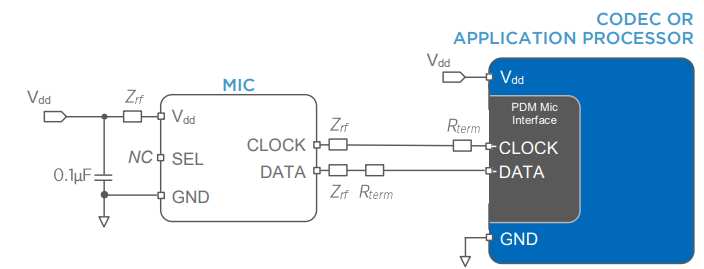
The PDM signal is later decimated and filtered by the audio codec or microcontroller to produce standard PCM audio data. This digital path avoids analog degradation and supports high-quality voice and sound capture even in electrically noisy environments.
Operating Modes
The SPK0641HT4H-1 operates in four distinct modes that depend on both the clock frequency (Fclock) and the supply voltage (VDD). These modes allow the microphone to balance performance and power efficiency according to system requirements.
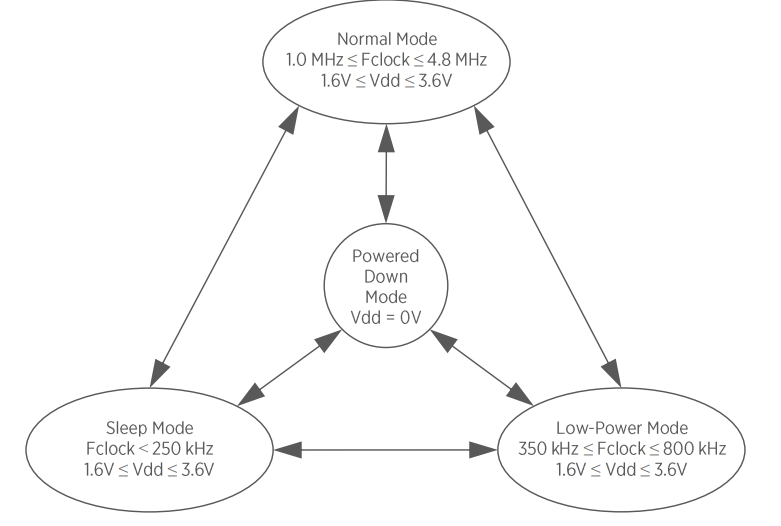
In Normal Mode, the clock frequency is between 1.0 MHz and 4.8 MHz with VDD = 1.6 V – 3.6 V.
This is the default full-performance state, providing maximum signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and sensitivity for high-quality audio capture.
When the clock frequency is reduced to between 350 kHz and 800 kHz, the microphone enters Low-Power Mode.
This mode reduces current consumption while maintaining functionality, making it ideal for always-listening or low-energy applications where slightly lower SNR is acceptable.
If the clock frequency falls below 250 kHz, the device transitions to Sleep Mode.
In this state, the internal circuits draw minimal current, and normal PDM output is halted until a valid clock resumes.
Sleep Mode provides an ultra-low-power standby condition for systems that periodically wake to record.
Finally, when VDD = 0 V, the device is in Powered-Down Mode, meaning all internal circuits are completely off and no data output occurs.
Reapplying the supply voltage and clock restores operation to the previous active state.
This mode architecture enables the SPK0641HT4H-1 to automatically manage power based on system conditions, delivering both efficiency and performance in portable or battery-operated designs.