BME688 Environmental Sensor - Taking measurements (MicroPython)
This page contains some simple examples with function documentation on how to take measurements using the BME688 sensor.
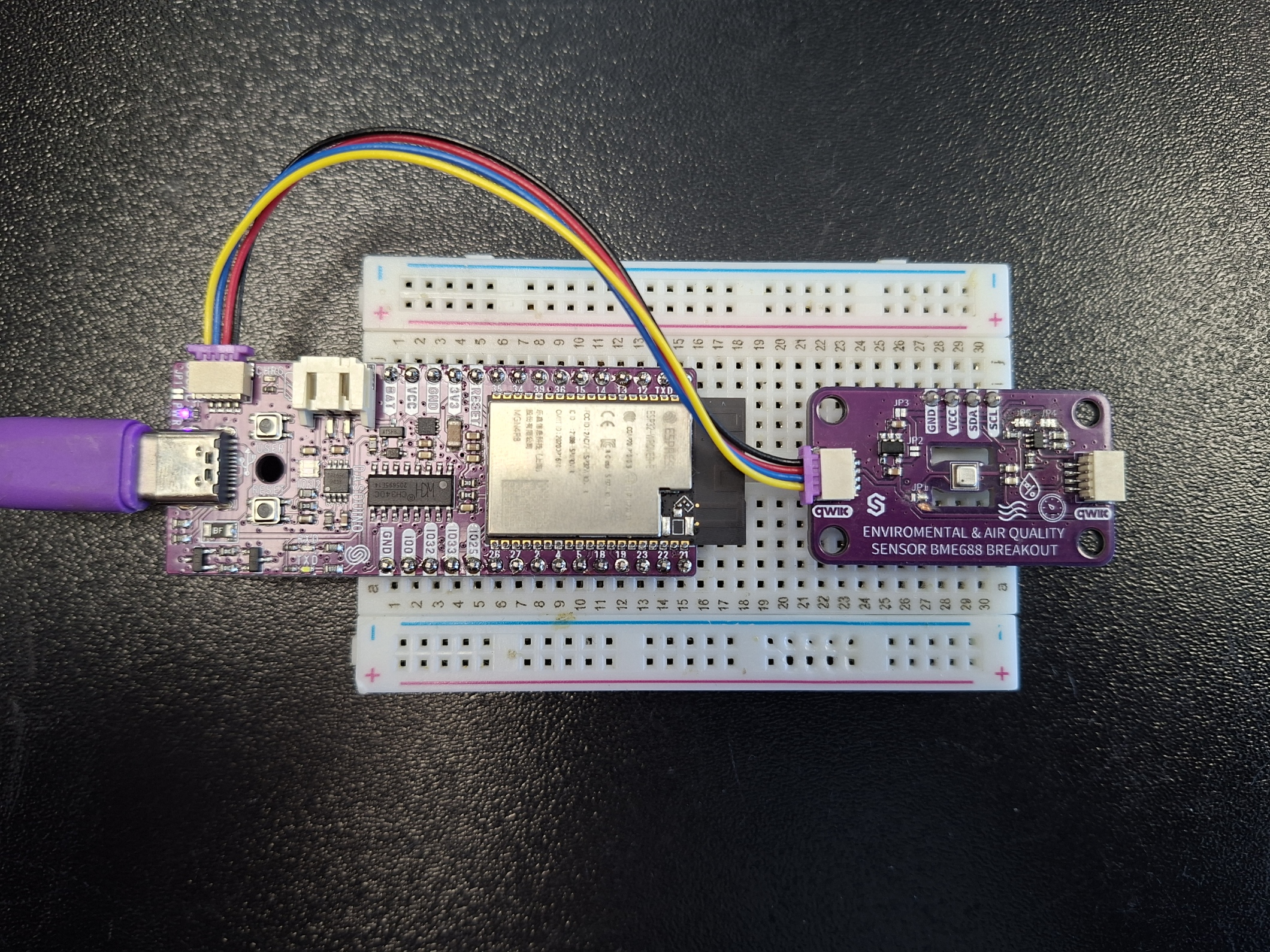
Connections for this example
Initialization
To use the BME688 sensor, first include the required module and create the sensor object
from bme688 import BME688
sensor=BME688()
Temperature
To get temperature value, use the readTemperature() function. The sensor samples temperature in degrees Celsius.
temperature=sensor.readTemperature()
print("Temperature: {:.2f}°C".format(temperature))
sensor.readTemperature()
Reads the value from the sensor and returns the scaled Celsius value
Returns value: Float value of the temperature reading in degrees Celsius
Pressure
To get pressure value, use the readPressure() function. The sensor samples the pressure in Pascals (Pa).
pressure = sensor.readPressure()
print("Pressure: {:.2f}Pa".format(pressure))
sensor.readPressure()
Float value of the temperature reading in Pa
Humidity
To get humidity value, use the readHumidity() function. The sensor samples humidity as a percentage.
humidity = sensor.readHumidity()
print("Humidity: {:.2f}%".format(humidity))
sensor.readHumidity()
Reads the value from the sensor and returns the scaled percentage value
Returns value: Float value of the humidity reading in %
Gas Resistance
To get gas resistance value, use the sensor.readGas() function. The sensor samples gas resistance in ohms.
gasResistance = sensor.readGas(0)
print("Gas Resistance: {:.2f}Ω".format(gasResistance))
sensor.readGas()
Reads the value from the sensor and returns the scaled value in ohms
Returns value: Float value of the gas resistance in ohms
Function parameters:
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
integer | profile | Selects which of the BME688's up to 10 configured heater profiles (0-9) |
Full example
In the full example we will import the time module so we can use the sleep() function. We will also import machine to use I2C and Pin hardware interfaces. Try all the above-mentioned functions in this full example, which prints the measured data over Serial every 2 seconds:
# FILE: bme688-readAllValues
# AUTHOR: Josip Šimun Kuči @ Soldered
# BRIEF: An example showing how to measure and read temperature, pressure, humidity as well as
# gas resistance using the BME688 sensor
# WORKS WITH: Environmental and Air Sensor BME688 Breakout: www.solde.red/333203
# LAST UPDATED: 2025-07-24
from bme688 import BME688 # Import BME688 module
from time import sleep # For delay between readings
from machine import I2C, Pin # Hardware interfaces
# Create sensor instance with default address and I2C Wiring
sensor = BME688()
# Initialize sensor with default settings
if not sensor.begin():
print("Failed to initialize sensor!")
else:
# Main measurement loop
while True:
# Read all environmental parameters
temperature = sensor.readTemperature() # °C
pressure = sensor.readPressure() # Pascals
humidity = sensor.readHumidity() # %RH
gasResistance = sensor.readGas(0) # Ohms (using profile 0)
# Print formatted measurements
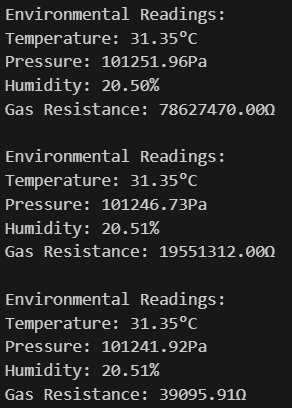
print("\nEnvironmental Readings:")
print("Temperature: {:.2f}°C".format(temperature))
print("Pressure: {:.2f}Pa".format(pressure))
print("Humidity: {:.2f}%".format(humidity))
print("Gas Resistance: {:.2f}Ω".format(gasResistance))
# Wait 2 seconds before next reading
sleep(2)