Microsd Reader - Reading binary files (example)
On this page, we will read binary data from an image
Preparation
To read from an image, we must first have an image. Load an image onto the SD card via a computer. For this example, we will use a screenshot from the previous example:
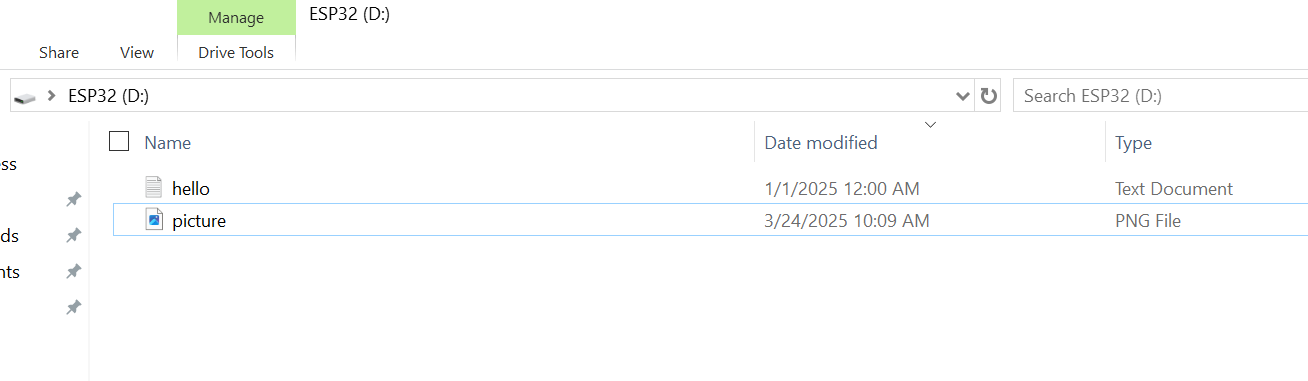
Next, we follow similar steps to the previous examples:
Defining the CS pin and instances
To write data to the SD card, we must first define, once again, the CS pin used for SPI communication (GPIO 5 in our case):
//...
// SDCARD_SS_PIN is defined for the built-in SD on some boards.
#ifndef SDCARD_SS_PIN
const uint8_t SD_CS_PIN = SS;
#else // SDCARD_SS_PIN
const uint8_t SD_CS_PIN = 5; //SET THIS PIN
#endif // SDCARD_SS_PIN
//...
We also have to create instances for the SD card and the file we will create, as well as a buffer for the binary data we are reading:
//Create an instance of the SD card
SdFs sd;
//Create an instance of the file system file object
FsFile file;
//Create a buffer which will hold 16 bytes
char buffer[16];
Reading binary data
First, we initialize the Serial communication; next, we initialize the SD card as well as its volume so that we can write and read data from it. Finally, we can read data from the SD card using the FsFile object:
void setup()
{
//Initialize the serial communication
Serial.begin(115200);
// Wait for USB Serial
while (!Serial)
{
yield();
}
Serial.println("Type any character to start");
while (!Serial.available())
{
yield();
}
// Initialize the SD.
if (!sd.cardBegin(SD_CONFIG))
{
sd.initErrorHalt(&Serial);
return;
}
if(!sd.volumeBegin())
{
Serial.println("Failed to initialize volume!");
return;
}
// Open the picture.
if (!file.open("picture.png", FILE_READ))
{
Serial.println("Failed to open file!");
return;
}
// Read the first n bytes, depending on the size of the buffer array
file.read(buffer, sizeof(buffer));
for(int i = 0; i < sizeof(buffer); i += 2)
{
// Print out the buffer values two at a time
Serial.print(buffer[i], HEX);
Serial.print(buffer[i + 1], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
// Close the file we were writing to.
file.close();
Serial.println("Reading from file done!");
}
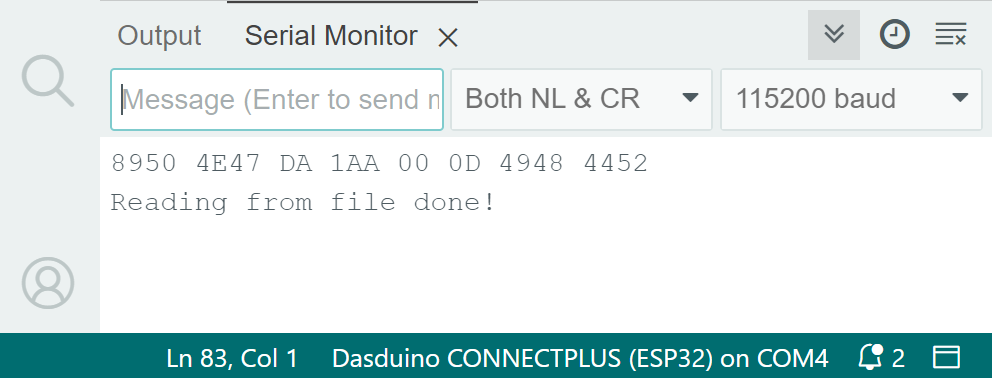
The output, depending on the chosen image, should look like this:
Full example
Below you can find the full example:
#include "SdFat.h"
//Set to one if there are more SPI devices connected to the bus
const int8_t DISABLE_CS_PIN = -1;
// SDCARD_SS_PIN is defined for the built-in SD on some boards.
#ifndef SDCARD_SS_PIN
const uint8_t SD_CS_PIN = 5;
#else // SDCARD_SS_PIN
const uint8_t SD_CS_PIN = SDCARD_SS_PIN;
#endif // SDCARD_SS_PIN
// Try to select the best SD card configuration.
#if HAS_SDIO_CLASS
#define SD_CONFIG SdioConfig(FIFO_SDIO)
#elif ENABLE_DEDICATED_SPI
#define SD_CONFIG SdSpiConfig(SD_CS_PIN, DEDICATED_SPI, SD_SCK_MHZ(16))
#else // HAS_SDIO_CLASS
#define SD_CONFIG SdSpiConfig(SD_CS_PIN, SHARED_SPI, SD_SCK_MHZ(16))
#endif // HAS_SDIO_CLASS
//Create an instance of the SD card
SdFs sd;
//Create an instance of the file system file object
FsFile file;
//Create a buffer which will hold 16 bytes
char buffer[16];
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setup()
{
//Initialize the serial communication
Serial.begin(115200);
// Wait for USB Serial
while (!Serial)
{
yield();
}
Serial.println("Type any character to start");
while (!Serial.available())
{
yield();
}
// Initialize the SD.
if (!sd.cardBegin(SD_CONFIG))
{
sd.initErrorHalt(&Serial);
return;
}
if(!sd.volumeBegin())
{
Serial.println("Failed to initialize volume!");
return;
}
// Open the picture.
if (!file.open("picture.png", FILE_READ))
{
Serial.println("Failed to open file!");
return;
}
// Read the first n bytes, depending on the size of the buffer array
file.read(buffer, sizeof(buffer));
for(int i = 0; i < sizeof(buffer); i += 2)
{
// Print out the buffer values two at a time
Serial.print(buffer[i], HEX);
Serial.print(buffer[i + 1], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
// Close the file we were writing to.
file.close();
Serial.println("Reading from file done!");
}
void loop()
{
}